Vegetable reproduction methods

How Do Vegetables Reproduce? Vegetables, like other plants, have two main methods of reproduction: sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. These methods allow vegetables to produce offspring and ensure the continuation of their species.
In this article, I will discuss the processes involved in both sexual and asexual reproduction in vegetables, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of each method.
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction in vegetables involves the fusion of male and female reproductive cells, resulting in the formation of seeds. This process requires the involvement of flowers, pollination, and fertilization.
Asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, does not involve the fusion of reproductive cells. Instead, it allows vegetables to produce offspring that are genetically identical to the parent plant.
This method is advantageous in certain situations, such as when environmental conditions are unfavorable for seed production or when a plant wants to quickly spread and colonize an area.
Sexual reproduction in vegetables
Sexual reproduction in vegetables begins with the production of flowers. Flowers are the reproductive structures of plants and contain both male and female reproductive organs. The male reproductive organ, called the stamen, produces pollen, while the female reproductive organ, called the pistil, contains the ovary where the seeds develop.
Flowers and pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the stamen to the pistil. This can occur through various methods, including wind, water, or the help of animals such as bees, butterflies, or birds. When a pollen grain lands on the stigma of the pistil, it germinates and grows a tube down to the ovary, where fertilization takes place.
Fertilization and seed production
Fertilization occurs when the male reproductive cells in the pollen combine with the female reproductive cells in the ovary. This fusion results in the formation of a zygote, which develops into an embryo within the seed. The ovary then matures and becomes a fruit, protecting the seeds and aiding in their dispersal.
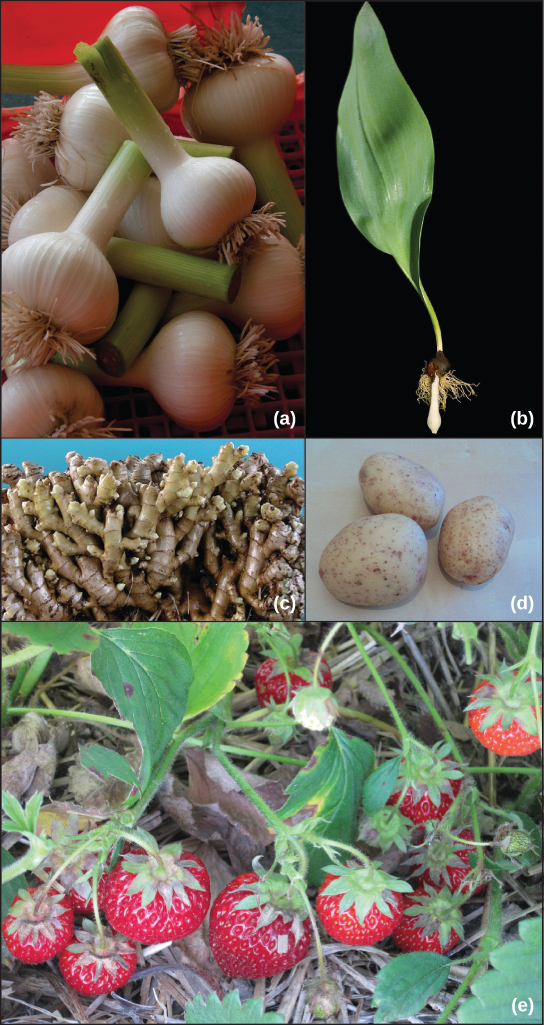
Asexual reproduction in vegetables

Asexual reproduction in vegetables does not involve the formation of seeds. Instead, it relies on vegetative propagation, where new plants are produced from vegetative parts of the parent plant, such as stems, leaves, or roots. This method allows plants to reproduce without the need for pollination or fertilization.
Vegetative propagation
Vegetative propagation can occur naturally or be induced by humans through various techniques such as cuttings, layering, or grafting. In natural vegetative propagation, plants can produce new shoots from their roots or develop new plants from their stems or leaves.
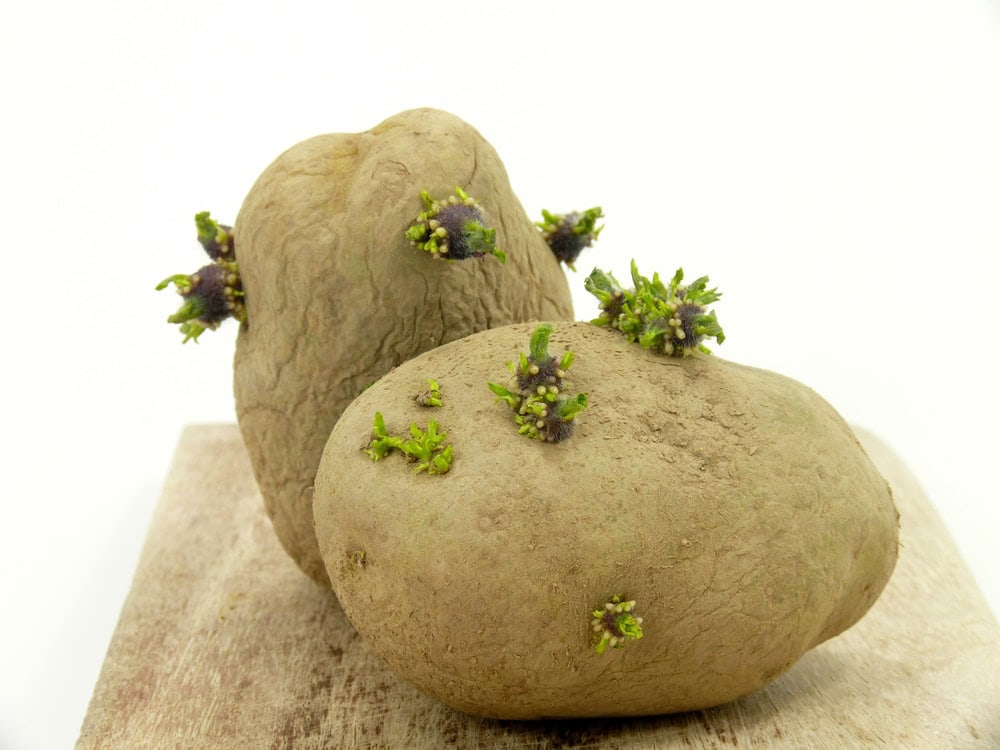
This method is commonly observed in plants like potatoes, where new plants can grow from the eyes or buds on the tubers.
Types of vegetative propagation
There are several types of vegetative propagation, including stem cuttings, leaf cuttings, root cuttings, layering, and division.
- Stem cuttings involve taking a portion of the stem with nodes and leaves and planting it to develop roots and grow into a new plant.
- Leaf cuttings, as the name suggests, involve using a leaf to produce a new plant.
- Root cuttings involve taking a portion of the root and planting it to develop new shoots.
- Layering is a method where a stem is bent and buried in the soil to develop roots, and once rooted, it can be separated from the parent plant.
- Division involves separating a clump of plants into smaller sections, each with its own roots and shoots.
Advantages and disadvantages of sexual and asexual reproduction

Both sexual and asexual reproduction have their advantages and disadvantages. Sexual reproduction allows for genetic diversity, which can be beneficial for plants to adapt to changing environments and resist diseases.
It also allows for the creation of new combinations of traits through the mixing of genetic material. However, sexual reproduction requires the involvement of pollinators and is dependent on favorable environmental conditions for successful seed production.
Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, allows for the rapid production of offspring without the need for pollination or fertilization. It ensures that the offspring are genetically identical to the parent plant, preserving desirable traits.
Asexual reproduction is also advantageous in situations where seed production is challenging, such as in plants that have sterile flowers or in environments with harsh conditions.
However, asexual reproduction does not allow for genetic diversity, which can make plants more susceptible to diseases and environmental changes.
Conclusion on How Do Vegetables Reproduce

In conclusion, vegetables can reproduce through sexual and asexual methods. Sexual reproduction involves the formation of flowers, pollination, and fertilization, resulting in the production of seeds.
Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, allows for the production of offspring without the need for seeds, through vegetative propagation. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, and plants may utilize different methods depending on their environmental conditions and reproductive goals.
Understanding the reproductive methods of vegetables can help gardeners and farmers make informed decisions when it comes to propagating and cultivating these plants.
FAQs on How Do Vegetables Reproduce
-
How do you grow vegetables if they don’t have seeds?
You can plant bean sprouts and they will grow into bean plants. You can plant cloves of garlic or onion hearts and they will reroot and grow. You can do stem cuttings from plants like basil and cilantro and they will root at the nodes and grow.
-
Do vegetables have seeds?
Vegetables are parts of plants that don’t involve flowers or seeds – for instance, potatoes are parts of the roots that store carbohydrate, lettuce is leaves. These plants make and grow from seeds.
-
How do you get seeds for vegetables?
To get seeds, leave developing pods on one plant until they are completely dried and brown. Next, cut the pods off the plant and place them in a cool, dark spot to dry further. Later, remove the seeds and spread them on cloth. Let them harden there for a few days.
-
What vegetables keep reproducing?
These seven vegetables can be grown as perennials in most zones: Globe artichokes, Asparagus, Jerusalem artichokes, Some members of the onion family, Radicchio, Rhubarb, Sorrel.
Originally posted 2023-11-09 03:32:33.

